What is TDEE?
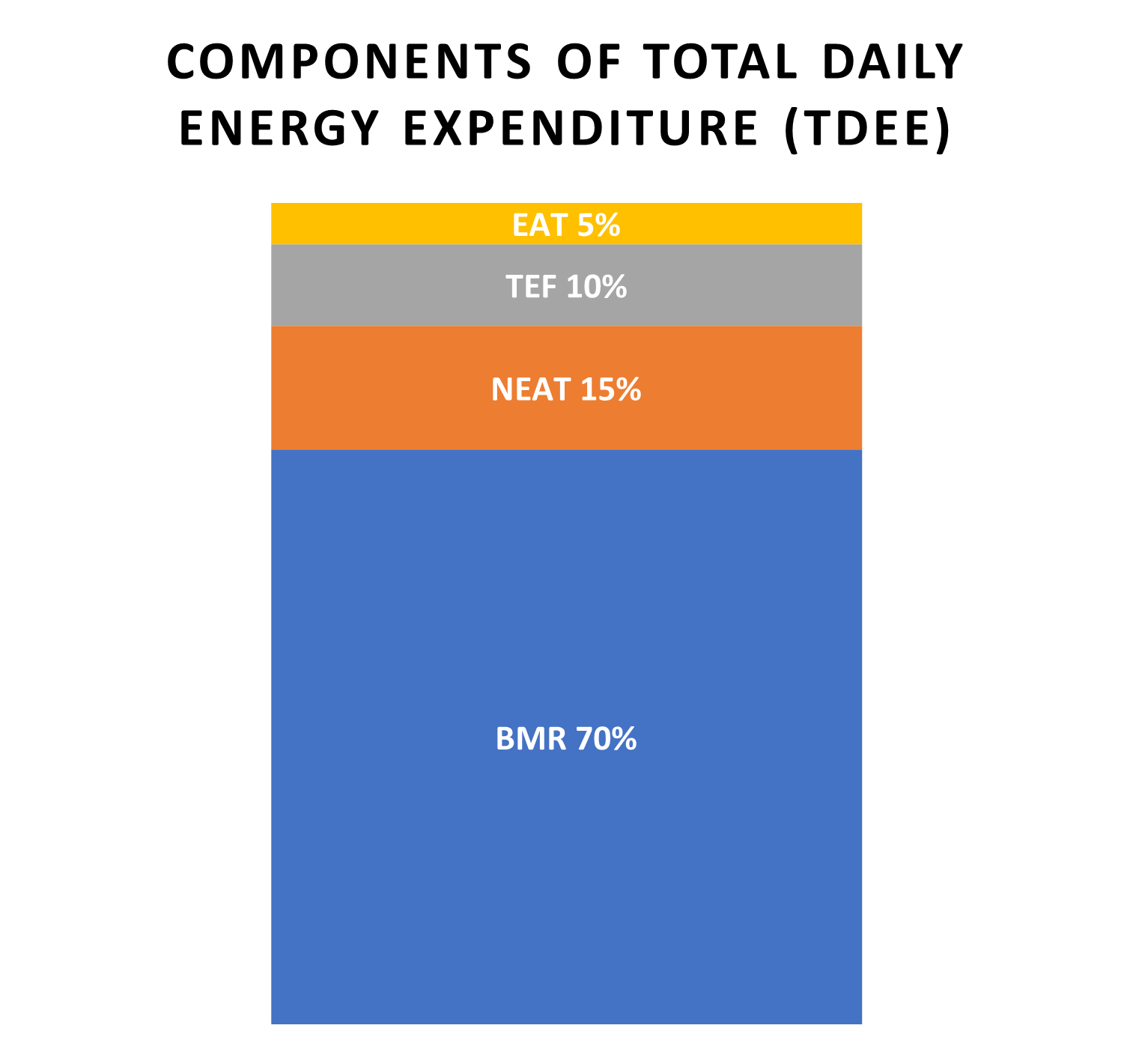 Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE) is a measure for the total amount of calories the human body burns through in a day.
Its biggest component is Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) - the amount of calories burned at rest.
Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE) is a measure for the total amount of calories the human body burns through in a day.
Its biggest component is Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) - the amount of calories burned at rest.
If you eat calories equal to your TDEE, you will maintain the same weight.
If you eat less calories than your TDEE, you will lose weight.
If you eat more calories than your TDEE, you will gain weight.
Measuring BMR officially must be done in a laboratory, but this calculator
can give an accurate estimate. The exact formulas used by this calculator to calculate BMR, and the other components of TDEE, are explained below.
NEAT and EAT refer to
'Non-Exercise Activity Thermogenesis' and 'Exercise Activity Thermogenesis' respectively. Both refer to
energy burned by using your body and being active. EAT typically refers to purposeful exercise such as going for a run or lifting weights, whilst NEAT would include activities
such as walking to work or climbing the stairs in your home.
The Thermic Effect of Food (TEF) measures the calories we burn in the digesting of food.
As the TDEE given by this website is just an estimate, you should weigh yourself regularly if you are dieting.
It is also important to make sure you have measured your calories correctly.
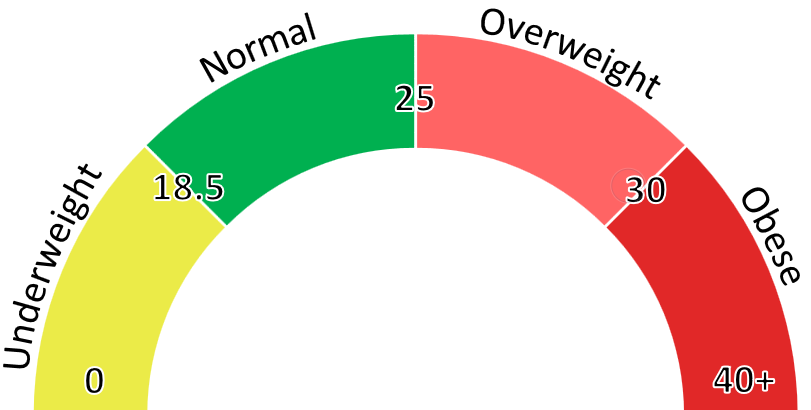
Understanding BMI
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a value calculated from a person's weight and height, to determine if the person is 'underweight', 'normal', 'overweight', or 'obese'.
Whilst it can be a useful 'rule-of-thumb' measurement, you should not necessarily take this number too seriously. It is a flawed measurement in the sense that it doesn't account for
the different body compositions of different individuals. For example, those with high levels of muscle and low-to-moderate levels of bodyfat might be deemed 'overweight' by BMI criteria, even though a good level of muscle mass is considered healthy.
How to Calculate Bodyfat %
Bodyfat % is the percentage of your body mass that is comprised of fat.
The most accessible method of measuring bodyfat is by purchasing skinfold calipers. These are relatively inexpensive, and just involve pinching fat between a device that measures the quantity of the fat.
There are a variety of other 'gold-standard', scientific methods of calculating bodyfat %, but the increase in accuracy you would gain by using those, as opposed to calipers, is negligible when using this calculator.
How Weight Loss/Gain are Calculated
There are approximately 3,500 calories in a pound of fat (7,700 in a kg of fat). These numbers are simply divided by the caloric deficit/surplus figures you toggle on the calculator to determine how much weight you will lose/gain per week.
Unlike some other calculators, this calculator does not let you enter a long-term weight goal when calculating how many calories to eat per day. The problem with doing so is that as you lose weight, your body mass drops, and consequently your TDEE will drop over time. The opposite is true for gaining weight. It is good to keep a long-term goal, but it is CRUCIAL that you regularly weigh yourself to see if you are still progressing towards your weight goal.
How Macros are Calculated
The macronutrients (macros) consist of carbohydrates, protein, and fats. Carbohydrates and protein contain 4 calories per gram, whilst fats have 9 calories per gram.
Based on your TDEE and the caloric surplus or deficit you choose, the resulting daily caloric consumption will be divided by the macro percentages you input on a calorie basis. Therefore you can calculate macros for weight loss, macros for muscle gain, or any other purpose.
Contact us
Please contact us with any queries or concerns via email at:
admin@tdeemacros.com